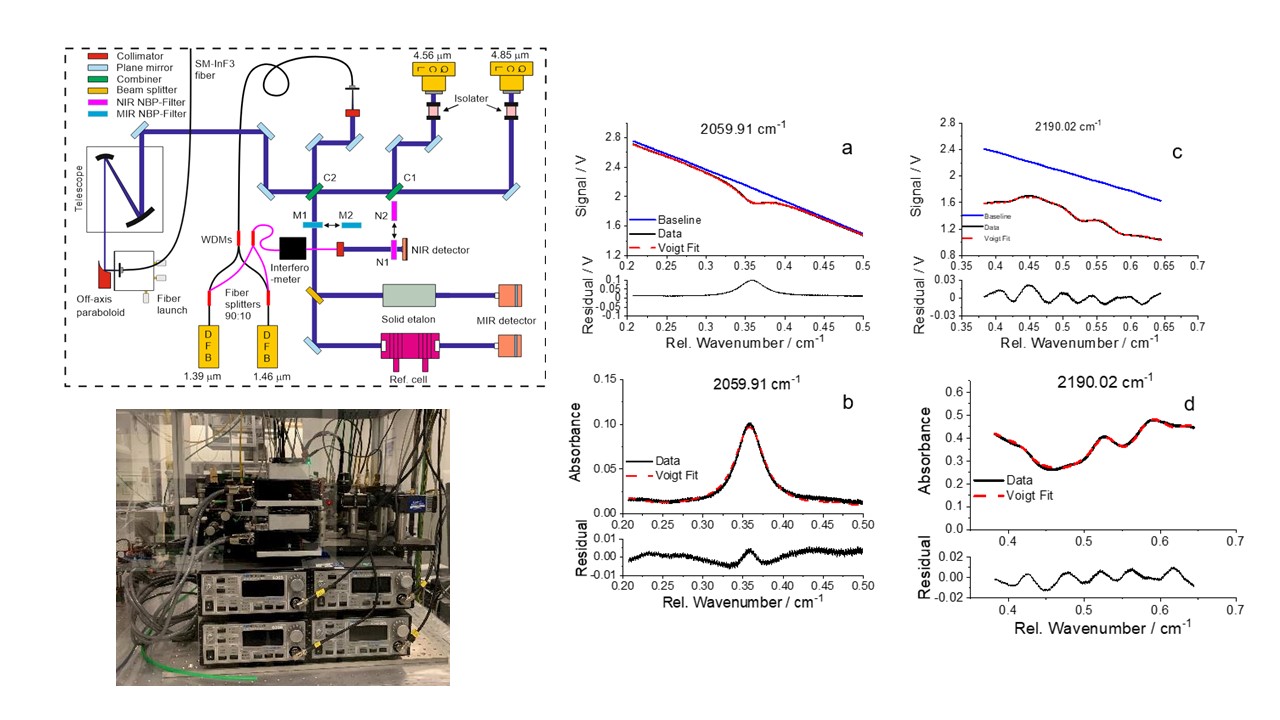
Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS) for process characterization
Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) is a highly precise and non-intrusive method for characterizing gas flows in various chemical and energy processes. This technique relies on the absorption of laser light by specific molecules in the gas phase, enabling accurate determination of concentrations and temperatures.
Fundamentals of TDLAS
TDLAS exploits the fact that certain gas molecules exhibit characteristic absorption lines in the near-infrared (NIR), visible, or ultraviolet (UV) spectral regions. A tunable diode laser is set to one of these absorption lines and directed through the gas. The absorbed light is measured and analyzed to obtain information about the concentration and temperature of the molecules in the gas.
The main components of a TDLAS system are:
- Tunable diode laser: Emits light at specific (tunable) wavelengths that are absorbed by the gas
- Absorption cell: The area where the gas to be measured is present
- Detector: Captures the light transmitted through the gas
- Control and analysis unit: Analyzes the absorption data to calculate concentrations and temperatures
Applications of TDLAS
Concentration measurements
TDLAS enables precise determination of gas species concentrations such as H₂O, CO, CO₂, NOₓ, and O₂ in flames and exhaust streams. This information is crucial for optimizing combustion processes and reducing pollutant emissions. By analyzing parts of the absorption spectra of these molecules, their concentrations can be measured in real-time with high accuracy.
Temperature measurements
The temperature of a gas can be determined by analyzing the linewidth and relative intensities of multiple absorption lines. TDLAS can detect these changes and calculate the gas temperature. This is particularly useful in flames, where accurate temperature profiles are needed for modeling and optimizing combustion processes.
Implementation in fiber optic probes
TDLAS can be implemented using fiber optic probes, allowing for flexible and remote measurements in harsh environments. Fiber optic probes can be inserted directly into combustion chambers, reactors, or other difficult-to-access areas, enabling in situ monitoring without disturbing the process. This makes TDLAS an invaluable tool for real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes.
Advantages of TDLAS
- Non-intrusive: Does not interfere with the process being measured
- High sensitivity: Capable of detecting low concentrations of gas species
- Real-time monitoring: Provides immediate data on gas concentrations and temperatures
- Versatility: Can be used in a wide range of applications, from laboratory research to industrial process control
In summary, TDLAS is a versatile and powerful technique for characterizing combustion processes and other chemical and technical processes. Its ability to provide accurate real-time measurements of gas concentrations and temperatures makes it an essential tool for understanding, improving, and controlling various industrial applications.