Research
Research Topics
Several research topics are associated to the Flagship Program Materials Chain of the UA Ruhr
Multiscale Modeling / Computational Homogenization |
 |
Electro- and Magneto-Mechanics |
 |
Coupled Problems |
 |
|
|
|
Finite-Element Technology |
 |
Biomechanics |
 |
Continuum Mechanics and Numerical Methods |
 |
|
|
Material Modelling |
|
|
|
|
Teaching |
|
|
|

CRC TRR 270 - Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - Projekt number 405553726 Scale-bridging of magneto-mechanical mesostructures of additive manufactured and severe plastically deformed materials
- Associated People:
J. Schröder, M. Reichel - Abstract:
Magnetic materials make a key contribution to the energy transition in a wide range of technical applications. For example, particularly powerful permanent magnets can be used for efficient transportation in electric cars or energy conversion by means of wind generators to help cut greenhouse gases that are a threat to the climate. The current gold standard in the field of permanent magnets, in terms of performance, are NdFeB magnets. They currently deliver the highest energy product, but are prone to corrosion and higher temperatures, at which they quickly suffer high performance degradation. By adding heavy rare earths (HRE), such as dysprosium or terbium, these properties can be improved. Since the mining of HRE has dramatic consequences for the environment and the world market price is also very volatile, one goal is to reduce the portion of these elements and replace them with other abundant elements. Besides the stoichiometric composition of the materials, the underlying microstructure also has a decisive influence on the magnetic behavior. New process routes, such as severe plastic deformation (SPD) or additive manufacturing (AM), are intended to better control the production and targeted influence of these microstructures in the future. In this context, finite element-based simulations may help to predict the properties and the performance of the considered magnets. The theoretical framework is provided by the micromagnetism, which models the behavior of the magnetization vectors in the context of a phase field, enabling local domain wall motions and pinning mechanisms to be studied as well. The main challenges here are the non-convex constraints on the magnetization length and the fine discretization of the microstructures, which can be highly heterogeneous. The overall aim of this research, within the framework of the CRC/TRR 270 HoMMage, is to tailor strong and efficient magnets for green energy conversion.
- References:
M. Reichel, B.-X. Xu and J. Schröder, A comparative study of FE-schemes for micromagnetic simulations, Proceeding in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 21, e202100191 (2021).
J. Schröder, M. Reichel and C. Birk, An efficient numerical scheme for the FE-approximation of magnetic stray fields in infinite domains, Computational Mechanics 70, 141-153 (2022).
C. Birk, M. Reichel and J. Schröder, Magnetostatic simulations with consideration of exterior domains using the scaled boundary finite element method, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 399, 115362 (2022).
M. Reichel, B.-X. Xu and J. Schröder, A comparative study of finite element schemes for micromagnetically coupled simulations, Journal of Applied Physics 132, 183903 (2022).
M. Reichel, J. Schröder and B.-X. Xu, Efficient micromagnetic finite element simulations using a perturbed Lagrange multiplier method, Proceeding in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, accepted (2022).
CRC TRR 270 - Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - Projekt number 405553726 Management of data obtained in experimental and in silico investigations
- Associated People:
J. Schröder, O. Gutfleisch (TU Darmstadt), R. Niekamp, M. Grönewald (TU Darmstadt)
- Abstract:
The collaborative research project SFB/TRR 270 "Hysteresis design of magnetic materials for efficient energy conversion" - HoMMage for short - is dedicated to the research of new magnetic materials for energy conversion. This includes both hard permanent magnets with maximized hysteresis, as well as soft magnets with minimized hysteresis. Both types have different applications, the former in the field of wind generators or electromobility, the latter in magnetic cooling using the magnetocaloric effect. What all these applications have in common is that they benefit from new magnetic materials that have been improved for the respective application. Therefore, within the SFB/TRR 270 researchers from different disciplines such as materials science, physics, chemistry or production engineering, distributed over several working groups at five locations, are looking for new innovative magnetic materials and ways to process them.
In addition to the classical paradigms, this multidisciplinary joint project is pursuing the data-driven approach to find new magnetic materials with improved properties. The INF subproject provides support in this regard, especially in questions of research data management(RDM), so that among other things the generated research results can be stored and exchanged in a centralized and structured way.
As a central service project within the SFB/TRR 270, INF aims to enable sustainable management of research data according to the FAIR principle for all stakeholders across sites. In an abstract view, besides purely infrastructural challenges, the most important ones are: complexity, heterogeneity and size of data. One of the first tasks was to define plans for data collection and management (so-called data management plans, DMPs). An electronic laboratory record book (ELB) based on free software (FLOSS) is available and will be continuously extended. Large parts of the resulting research data can be loaded and shared via it and can be found via a user interface according to basic criteria. Via an interface, the content is available for automated data conversion and reduction.
In conjunction with a storage infrastructure and interfaces for particularly large research data, it is part of the necessary toolkit to analyze the collected research data and metadata using machine learning algorithms to discover new material. One other essential task for INF is to provide training to all members of SFB/TRR 270 on topics related to FDM through regular workshops and consultation, and to raise awareness of possible improvements in data handling. To prevent silo thinking, the integration of data and tools into the broader FDM landscape is also an important issue. Many challenges are posed to RDM within an interdisciplinary collaborative project.
In addition to technical requirements and incompatibilities in the integration of existing infrastructure, collaboration between the technically heterogeneous groups also generates new, and in some cases specialized, needs. The INF project within the SFB/TRR 270 HoMMage aims at meeting these challenges with a combination of self-managed and centralized infrastructure, as well as the task to provide knowledge and support to the researchers within the network for a better RDM, and the claim of a scientific reuse in the context of artificial intelligence. Thus, with the help of structured research data and modern computer methods, a successful contribution can be made to the development of new promising magnetic materials can be delivered.
- References:
Tolle, Kristin M.; Tansley, D. Stewart W.; Hey, Anthony J. G. (August 2011). "The Fourth Paradigm: Data-Intensive Scientific Discovery [Point of View]". Proceedings of the IEEE. 99 (8): 1334–1337. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2011.2155130
C. Draxl, M. Scheffler, NOMAD: The FAIR concept for big data-driven materials science, MRS Bulletin, 43, 676-682, 2018. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1805.05039
M. D. Wilkinson, et al., The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship, Sci. Data 3, 2016. doi:10.1038/sdata.2016.18
>>TOP<<
SPP 2256 - Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - Project number 440935806, SCHR 570-39-1, SCHE 2134-1-1, NE 902-10-1 A variational scale-dependent transition scheme: From Cauchy elasticity to the relaxed micromorphic continuum
- Associated People:
J. Schröder, L. Scheunemann, M. Sarhil, P. Neff
- Abstract:
Mechanical metamaterials are a fast-growing field in industrial applications due to their specially tailored macroscopic behavior. The analysis and modelling of metamaterials, which exhibit exotic properties including band gaps, negative refraction, dispersion or cloaking, requires higher-order continua to capture size effects arising from complex microstructures. In this research project, we follow a new and promising approach based on the relaxed micromorphic model [1], which is able to describe "exotic" properties on the macroscopic scale in a variationally consistent way. The relaxed micromorphic model reduces the complexity of the general micromorphic theory utilizing fewer material parameters by implementing the Curl of the micro-distortion field with keeping the full kinematics of the micromorphic theory. We aim to analyze macroscopic boundary value problems with fully resolved microstructures and compare it to the macroscopic relaxed micromorphic model using H(Curl) conforming finite elements [2]. Then suitable formulations are extracted from these evidence-based findings for an extension of a macro-homogeneity (Hill-Mandel) condition. This allows for a rigorous energetically and mathematically consistent scale-dependent homogenization scheme, connecting the relaxed micromorphic continuum (macroscale) with the associated Cauchy continuum (microscale).
- References:
[1] P. Neff, I.D. Ghiba, A. Madeo, L. Placidi, G. Rosi. A unifying perspective: the relaxed linear micromorphic continuum. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 26,639-681(2014).
[2] J.C. Nédélec, Mixed finite elements in R3, Numer. Math. 35,315-341(1980).

SPP 2013 - Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - Projekt number 374871564 Experimental and numerical modeling and analysis of microstructural residual stresses in hot bulk forming parts under specific cooling
- Associated People:
J. Schröder, B.-A. Behrens (Hannover), D. Brands, L. Scheunemann, R. Niekamp, A. Chugreev (Hannover), C. Kock (Hannover), S. Uebing, M. Sarhil - Abstract:
The consideration of residual stresses in metallic components produced by forming has primarily been undertaken with a view only to avoid or minimize them so far in order to improve the durability and manufacturability. A targeted use for improvement of properties e.g. the operational strength in the field of forming technology has so far received little attention.The aim of this project is to investigate the various influences on distribution and stability of the residual stress development in thermo-mechanically processed components by means of controlled cooling in both the experiment as well as the numerical simulations. In the long term, the goal is to optimize the forming process in such a way that a targeted use for improvement of the properties of the component becomes possible. A precise representation of the residual stresses, their development in numerical simulation as well as their interpretation in experimental results requires a profound knowledge of the thermal, mechanical as well as metallurgical properties of the used material. For this reason, in addition to the characterization of the microstructure transformation behavior, extensive investigations of the thermomechanical deformation behavior will be carried out.As an experimental demonstrator component, a cylindrical sample with an eccentric drilled hole will be considered, which will be isothermally compressed in a forming simulator and subsequently cooled in a targeted manner. The eccentric upsetting specimen evokes an inhomogeneous residual stress state, thus enabling the targeted investigation of different cooling scenarios. The numerical modeling of the residual stresses requires a multiscale view because of their classification into of 1st, 2nd and 3rd type. A macroscopic, phenomenological description in the framework of the Finite Element Methods (FEM) taking into account the thermo-mechanical and metallurgical properties will be used for the representation of the residual stresses of the 1st kind whereas, the phasefield theory and the FEM will be used to model the microstructural residual stresses (2nd and 3rd type). The microstructural transformation will be simulated by means of a phase-field model and representative volume elements will be created, which are to be used for the subsequent FEM simulations on the microscale.The close interaction between experiment and numerical simulation allows the calibration and validation of models and material descriptions during the first step. In the long term, a methodology is to be developed which will allow a deeper understanding of the phenomena occurring in the material and their relationship to the resulting residual stresses. From these findings, the process and simulation parameters can be modified in such a way that after cooling a stable residual stress distribution, which positively influences the properties of the component, can be produced in the workpiece. - References:
Behrens, B.-A. und Olle, P. 2008. Consideration of transformation-induced stresses in the
simulation of press hardening. Proceeding of International Plasticity. 2008.Brands, D., et al. 2016. Computational modeling of dual-phase steels based on representative
three-dimensional microstructures obtained from EBSD data. Archive of Applied Mechanics.
2016, Bd. 86, 3, S. 575-598.Steinbach, I. 2009. Phase-field models in materials science. Modelling and Simulation in
Materials Science and Engineering. 2009, Bd. 17, 7, S. 073001.
>>TOP<<

Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - Projekt number 342697063 Least-squares fluid-structure-interaction for incompressible flows
- Associated people:
A. Schwarz, J. Schröder, S. Averweg und C. Nisters - Abstract:
The proposed research project aims to develop, construct and analyse least-squares finite element methods (LSFEM) in fluid- and solid mechanics. The proposed mixed element formulations are given in stresses and velocities and are supposed to be used in a new method of fluid-structure interaction (FSI). Current FSI approaches include a certain treatment of the interface between solid and fluid phase in order to guarantee the equality of the mentioned quantities along this interface. In the proposed FSI approach these interface conditions are fulfilled intrinsically by the choice of the interpolation spaces and are considered automatically.The LSFEM results in stable formulations for first order systems and is applied successfully especially in fluid mechanics. The construction of the finite elements leads to positive definite and symmetric system matrices, also for differential equations with not self-adjoint operators. Furthermore, the method is not restricted to the LBB-condition, such that a free choice of the polynomial degree of the interpolating functions is possible. This increases the number of possible combinations in the construction of the finite elements.Essentially, the proposed research project can be subdivided into three periods. First, in a preinvestigation the central idea of the FSI coupling is analysed for a small strain model. This is the fundament for the following stage of constructing and developing the proposed mixed finite elements for the fluid and solid phase considering finite deformations and instationarities. The stress-velocity formulations are investigated with respect to reliability and efficiency. Special focus rests on the approximation quality of the solution variables and the robustness of the formulations. Finally, the least-squares FSI approach has to be validated with help of known benchmark problems. The research project is supposed to point the way in the regime of non-conventional discretization methods solving fluid-structure-interaction problems.
- References:
Nisters C, Schwarz A, Averweg S and Schröder J (2018), "Remarks on a
Fluid-Structure Interaction scheme based on the least-squares finite
element method at small strains", Advances in Mechanics of Materials and
Structural Analysis. Advanced Structured Materials 80, pp 261-279,
Springer.Schwarz A, Nisters C, Averweg S and Schröder J (2018), "Stress-Velocitiy
Mixed Least-Squares FEMs for the Time-Dependent Incompressible
Navier-Stokes Equations", In Large-Scale Scientific Computing. Lecture
Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 10665, pp. 137-144. Springer.Nisters C and Schwarz A (2018). "Efficient stress–velocity least-squares
finite element formulations for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations".
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 341, 333–359.
A Stochastic Model for Strong Wind Events in Central Europe based on Historical Wind Data
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, R. Niekamp, D. Brands, C. Götzen, M. Kiseleva, J. Niekamp, O. Siems - Abstract:
Due to the European directive 'Solvency II' insurance companies need to estimate the possible claims for their individual portfolio for a 200 year event. The total loss amount includes estimations for losses suffered from natural catastrophes such as windstorms. For this task there exist a couple of commercial tools. Theyare based on physical models of wind appearance or they just work with distortions of historical hazards. In contrast to the approaches of the existing commercial simulation tools we develop in this project a purely data driven model. From the available historical data we extracted the hourly wind peeks measured at 400 weather stations in Central Europe over the last two decades. After a normalization of these data, removing the geographical exposure of the measure points, we generated a set of uncorrelated wind fields.
These wind fields are used to get a Polynomial Chaos expansion of the stochastic wind field by a recombination of these fields with stochastic coefficients. The stochastic coefficients themselves are constructed by multi-variate Hermite-polynomials with unknown deterministic coefficients. The equations for these latter coefficients are found by forcing the identity of a suitable set of mixed moments of the wind history and the stochastic model. The Quasi-Newton method is used to solve the arising highly non-linear equations.arising highly non-linear equations. The generation of the random wind-events with this stochastic model is computational very cheap. In the time scale of hours we can, using the Monte Carlo method, simulate 10^9 years of insurance risk due to wind hazards.

The possibility of improving individual learning processes by digital pre-study and introductory phase for civil engineering students
- Associated poeple:
Jörg Schröder, Martin Lang, Yasemin Özmen, Marcel Pelz, Felix Walker, Ralf Müller and Julia Christmann - Abstract:
In many higher educational engineering courses, a high number of drop outs can be observed. This can often be explained by performance problems within the introductory phase of the studies. Especially in basic subjects, such as engineering mechanics or engineering mathematics, the performance problems are to be seen as a decisive factor. In order to counteract this problem and provide the chance to prepare the students for their upcoming studies, the project FUNDAMENT focuses on a support concept that intervenes preventively in the preliminary and the introductory phase of the civil engineering studies using digital higher education. By providing an online self-assessment and an online prep course, knowledge gaps can be identified and closed in the preliminary phase. Furthermore, online exercises with immediate checking and feedback as well as learning videos are utilized in the introductory phase of the civil engineering studies and provide additional study matter. A longitudinal study is set up using performance tests in the first and second semester and show the impact of the used digital learning elements on the performance of the students.
-
References:
Behrendt, S., Dammann, E., Ștefănică, F., Markert, B., & Nickolaus, R. (2015). Physical-technical prior competencies of engineering students. Empirical Research in Vocational Education and Training, 7(1), 121. doi:10.1186/s40461-015-0013-9.Berger, M. & Schwenk, A. (2006). Zwischen Wunsch und Wirklichkeit: Was können unsere Studienanfänger?. In: Die neue Hochschule, 2, S. 36-40.
Fischer, P. R. (2014). Mathematische Vorkurse im Blended-Learning-Format: Konstruktion, Implementation und wissenschaftliche Evaluation. Wiesbaden: Springer Spektrum.
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) SPP (German Priority Program) 1748 Novel finite elements - Mixed, Hybrid and Virtual Element formulations at finite strains for 3D applications
-
Associated poeple:
J. Schröder and N. Viebahn in cooperation with P. Wriggers (Leibniz University Hannover) and A. Kraus. -
Abstract:
In this research project, the main goal is to develop new finite-element formulations as a suitable basis for the stable calculation of modern isotropic and anisotropic materials with a complex nonlinear material behavior. In order to achieve this goal new ideas are pursued in a strict variational framework since there is no obvious approach available at the moment. Three main strategies are followed. The fundament of the first strategy constitutes a novel extension of the classical Hellinger-Reissner formulation to non-linear applications. Herein, the constitutive relation of the interpolated stresses and strains is determined with help of an iterative procedure. This will be done on the basis of polyconvex strain energy functions. In a further step the discretization of the stresses is done by special interpolation functions, which guarantee the continuity of the traction vector over element edges. An alternative formulation, incorporating continuity of the traction vector, is part of the second strategy. The compliance of the balance of momentum is demanded on each subdomain. This leads to a primal formulation, which does not admit jumps of the traction vector.The extension of the promising virtual finite element method (VEM) is part of the third strategy. Particularly, further investigations in the stabilization method will be done, which are needed in the framework of complex nonlinear constitutive behavior. Furthermore the interpolation functions for the VEM will be extended from linear to quadratic functions to obtain better convergence rates. In addition, the VEM will be extended, formulated and implemented for 3D applications in order to use the method in the framework of crystal plasticity. Especially in this application the flexibility of the VEM regarding the mesh generation will constitute a huge benefit.As a common software development platform the AceGen environment is applied providing a flexible tool for the generation of efficient finite element code.

Mikromechanische Modellierung der Materialumformung zur Vorhersage der anisotropen Verfestigung
- Associated People:
J. Schröder, A. Hartmaier, A.E. Tekkaya, N. Vajragupta, D. Brands, S.F. Maassen, T. Clausmeyer - Abstract:
In der Umformtechnik wird derzeit hauptsächlich auf phänomenologische Materialmodelle zurückgegriffen, die zwar eine quantitative Beschreibung von Umformvorgängen erlauben, aber keine Informationen über die Mikrostruktur des Werkstoffs und die grundlegenden Mechanismen der Umformung beinhalten. Darum müssen solche Modelle für jeden Werkstoff und jeden Werkstoffzustand aufwendig parametrisiert werden. Neuartige Ansätze zur mikromechanischen und skalenüberbrückenden Materialmodellierung haben das Potential hier eine signifikante Verbesserung zu erzielen, so dass zukünftig der Einfluss von mikrostrukturellen Parametern auf Umformeigenschaften vorhergesagt werden kann und im Umkehrschluss auch das Design von Mikrostrukturen mit spezifischen Umformeigenschaften möglich wird. In dem beantragten Forschungsvorhaben sollen zwei verschiedene Ansätze zur mikromechanischen und skalenüberbrückenden Werkstoffmodellierung darauf angewandt werden, Blechumformung bei Raumtemperatur zu beschreiben. Im Fokus der Forschung liegt hier insbesondere die Beschreibung und mikrostrukturspezifische Vorhersage der anisotropen Verfestigung bei der Umformung, durch die es in unterschiedlichen Raumrichtungen zu unterschiedlichen Umformgraden und verschieden starken Rückfederungsprozessen kommt. Ein Verständnis solcher Vorgänge auf mikrostruktureller Basis ist nicht nur von hohem wissenschaftlichem Interesse, sondern führt auch zu einem verbesserten Prozessverständnis und technologischen Neuerungen in der Umformtechnik.
Modeling of ionic electroactive polymers consistent formulation of the thermoelectro-chemo-mechanical coupling effects and finite-element discretization
- Associated People:
J. Bluhm, J. Schröder, S. Serdas - Abstract:
Multifunctional materials as the Electroactive Polymers (EAPs) belong to the class of smart materials. These materials can change their properties due to external influences and/or active energy supply. Inspired by the behavior of biological systems, the development and manufacture of EAPs in view of new applications in engineering, material science and medicine is a subject of international research. The aim of the research project is the development of a continuum-based model and its algorithmic implementation for the description of the behavior of ionic EAPs. These materials consist of a network of polymer fibers, the pore space is filled with liquid and cations. The deformation of ionic EAPs is driven by the motion of the cations (diffusion) triggered by an electric field. An advantage of ionic EAPs is that only a few volts are needed for the actuation, the disadvantage is that they must be kept moist. For the continuum mechanical based description of the behavior of these multiphase materials, consisting of the phases solid (polymer matrix), liquid and ions, the Theory of Porous Media will be used. In view of the electro and thermo-chemomechanical coupling effects in ionic EAPs, the balance equations of electrodynamics will be considered. Predictions concerning an efficient mode of action of the ionic EAPs depending on the humidity of the polymer matrix shall be enabled. - References:
J. Bluhm, S. Serdas and J. Schröder [2016], "Theoretical framework of modeling of ionic eaps within the Theory of Porous Media", Archive of Applied Mechanics
P. Leichsenring, S. Serdas, T. Wallmersperger, J. Bluhm and J. Schröder [2017], "Electro-chemical aspects of IPMCs within the framework of the Theory of Porous Media", Smart Materials and Structures
>>TOP<<
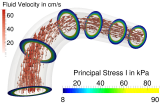
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project SCHR 570/15-2, in cooperation with SNF (Swiss National Science Foundation) under the D-A-CH agreement Domain-Decomposition-Based Fluid Structure Interaction Algorithms for Highly Nonlinear and Anisotropic Elastic Arterial Wall Models in 3D
- Associated people:
Jörg Schröder and Simon Fausten in cooperation with Axel Klawonn (University of Cologne), Daniel Balzani (RU Bochum), Oliver Rheinbach (TU Freiberg) and Simone Deparis (EPF Lausanne) - Abstract:
Transmural stress distributions of in vivo arteries are a major factor driving, e.g., the processes of arteriosclerosis and arteriogenesis. Realistic predictions for transmural stress distributions require a dynamic simulation considering the interaction of the blood flow with the vessel wall. One cannot expect to obtain precise predictions for vessel wall stresses using solid models that do not reflect the global layer structure and the anisotropic fibrous microstructure of the vessel wall. The fluid-structure-interaction (FSI) problem is known to be a nontrivial problem especially when nonlinear models are used for the structural part describing the deformation of the arterial wall. In this project, algorithms for the fluid-structure interaction are developed based on domain decomposition methods and applied to the computation of realistic transmural stresses in physiological models of arterial walls. The associated systems of coupled nonlinear partial differential equations are to be solved in 3D and on different parallel machines. Moreover, a biologically motivated model for the incorporation of fiber reorientation is taken into account. - References:
Balzani, D.; Deparis, S.; Fausten, S.; Forti, D.; Heinlein, A.; Klawonn, A.; Quarteroni, A.; Rheinbach, O. & Schröder, J. (2015), "Numerical modeling of fluid-structure interaction in arteries with anisotropic polyconvex hyperelastic and anisotropic viscoelastic material models at finite strains", International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 32(10), DOI: 10.1002/cnm.2756Fausten, S.; Balzani, D. & Schröder, J. (2016), "An Algorithmic Scheme for the Automated Calculation of Fiber Orientations in Arterial Walls", Computational Mechanics,
58(5), 861-878

DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) Project AN1113/2-1, BR5278/2-1, SCHR570/32-1 within the SPP (German Priority Program) 2020 Effects of Steel-fibers on the Degradation of High-Performance Concrete subjected to Fatigue Loading - Testing and Modeling
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, D. Brands, M. Pise in cooperation with S. Anders, G. Gebuhr (Bergische Universität Wuppertal)
- Abstract:
Systematic investigations of the deterioration of high- (HPC) and ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) subjected to fatigue loading are currently not available. This holds especially true for steel-fiber modified HPC and UHPC. Furthermore, numerical approaches and models are often calibrated using experimental data from literature, which does not allow a comprehensive calibration due to lacking coordination between experiments and numerical models. Therefore, this project aims at testing, describing and modeling the ongoing deterioration of steel-fiber modified HPC and UHPC subjected to fatigue loading, using multiscale approaches and phase-field theory. Here, two common concrete mixtures are applied: (i) HPC with a strength category C50/60 and (ii) UHPC with a compressive strength of about 150 MPa. The HPC will be modified using hooked-end steel-fibers with contents ranging from 23 kg/m² to 115 kg/m³, whereas the UHPC will contain short, straight high-strength fibers with contents ranging from 57 kg/m³ to 115 kg/m³.The fiber performance in the concrete matrix will be investigated in pull-out tests on single fibers. Additionally, static and cyclic 3-point-bending tests as well as cyclic uniaxial compression tests will be performed comparing fiber-free and fiber modified mixtures of the mentioned concretes each considering different load-levels. From these tests, damage indicators such as development of strain, stiffness or dissipated energy will be calculated and used to describe damage evolution using a strain-based formulation. Furthermore, a comprehensive energy function controlling the material degradation for a macroscopic model will be developed and implemented.Numerical simulations based on multiscale approaches are used for modelling and prediction of the macroscopic material behavior. On the mesoscale an ellipsoidal unitcell, serving as a representative volume element consisting of concrete matrix with a single embedded fiber, will be constructed and calibrated. In order to reduce complexity of the macroscopic simulations, an effective material model including an orientation distribution function for the fibers is constructed. The damage localization and crack propagation are modelled using the Phase-field Theory.An Experimental-Virtual-Lab approach, which is represented by the planned working program will be evaluated and optimized finishing the first funding period. Based on this approach a procedure evaluating fatigue performance of general (U)HPC mixtures will be developed, combining only a couple of experiments together with numerical techniquesHomepage Priority Programme 2020
https://www.spp2020.uni-hannover.de/

DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) SPP (German Priority Program) 1748 Approximation and reconstruction of stresses in the deformed configuration for hyperelastic material models
- Associated people:
Jörg Schröder, Maximilian Igelbüscher, in coorperation with Gerhard Starke, Fleurianne Bertrand, Marcel Moldenhauer, Gonzalo Gonzalez de Diego
- Abstract:
The goal of this project is to provide an improved understanding of elastic behavior at finite strains by promising finite element approaches which have so far mostly been studied in the context of linear elasticity. In particular, these include nonconforming $P_2$ elements on triangles and tetrahedra which have advantageous properties with respect to local momentum conservation and inf-sup stability. Our plan is to investigate how much of these favourable properties carry over to the hyperelastic situation. Momentum-conservative stresses can be reconstructed from displacement-pressure approximations using computations on local patches. In the case of hyperelastic material models, the reconstruction is somewhat more involved since the input stress arising directly from the displacement-pressure approximation is not piecewise linear anymore. Much more severe, however, are the difficulties associated with the use of these stress reconstructions to provide an a posteriori error estimator. The nonlinearity of the problem makes the situation much more complicated and we attempt to widen the range of applicability as much as possible.Approaches which compute stress approximations directly in $H (\operatorname{div})$-conforming finite element spaces will also be studied from the mathematical as well as from the mechanical side. To this end, least-squares finite element methods will be modified concerning the treatment of stress symmetry and the enforcement of inter-element continuity conditions. Finally, we will focus our attention on the Hellinger-Reissner principle for the direct computation of stress approximations which are momentum-conservative. For all these approaches, parametric Raviart-Thomas finite element spaces lend themselves for the approximation of the Cauchy stresses using a formulation that is completely set in the current (deformed) configuration.
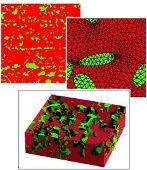
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project no SCHR 570-8/2 (research group 797 "microplast") Construction of Statistically Similar Representative Volume Elements (SSRVEs)
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, D. Balzani (TU Dresden), D. Brands, L. Scheunemann
- Abstract:
Micro-heterogeneous high-tech steels enable ambitious engineering constructions. For the design of such random multi-phase microstructures numerical simulation procedures are important for the reliable prediction of the overall response of macroscopic boundary value problems. Direct homogenization schemes, which are designed for such kind of problems, can only be efficient if the complex random microstructure is approximated by significantly less complex representative volume elements (RVEs) capturing the basic morphological attributes of the microscale. This is the main task in the project, where several statistical measures (spectral-density, lineal-path function, Minkowski valuations, etc.) are applied for the construction of statistically similar RVEs (SSRVEs). A main challenge in this period is the design of three-dimensional SSRVEs based on the Electron-Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) combined with Focused-Ion-Beam (FIB) measurements. The performance of the direct homogenization approach using the constructed SSRVEs is analyzed for representative macroscopic deep-drawing processes.
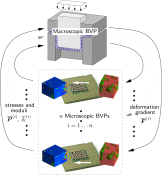
FE²-Simulations of Metall Forming Processes
-
Associated people:
J. Schröder, D. Balzani (TU Dresden), D. Brands
-
Abstract:
Advanced high strength steels are suitable materials to optimize stability while reducing weight. During the process of manufacture the material exhibits large plastic deformations. Since the distinct microstructure is a crucial reason for the material properties, its incorporation during the numerical analysis is necessary. A numerical tool for the direct incorporation of micromechanical information is the FE2-method, also known as direct micro-macro-transition procedure. Thereby in each macroscopic integration point a boundary value problem is solved on the microscale, where a representative volume element covers the typical morphology of the considered material.
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project SCHR570/19-1 within the SPP (German Priority Program) 1648 "SPPEXA" EXASTEEL - Bridging Scales for Multiphase Steels
-
Associated people:
J. Schröder, D. Balzani (TU Dreden), D. Brands, A. Gandhi in cooperation with A. Klawonn, M. Lanser (Universität zu Köln), O. Rheinbach(TU Freiberg), G. Wellein (Universität Nürnberg-Erlangen)
-
Abstract:
The project EXASTEEL in the SPP 1648 deals with the computational simulation of advanced high strength steels, incorporating phase transformation phenomena at the microscale using the FE² direct multiscale approach. Thereby in each macroscopic integration point an additional (microscopic) boundary value problem is solved and suitable volume averages of the microscopic responses replace the macroscopic constitutive set of equations compared to classical FEM computations. In a serial set-up this procedure results in high numerical costs especially in the three dimensional case. New, highly efficient, parallel solver algorithms will enable the FE² approach to perform simulations of three dimensional multiscale material science problems. Due to the main objectives of SPPEXA, here the development for the exascale computing on future supercomputers is one of the main aspects. - Homepage Project EXASTEEL
- Homepage SPPEXA Priority Programme 1648
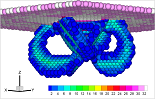
Atomistic-Continuum Coupling based on a Variationally Consistent Quasi-Continuum (QC) Method with Energy-Sampling in Clusters
- Associated people:
B. Eidel, A. Stukowski (LLNL, USA), J. Schröder
- Abstract: The quasi-continuum (QC) method is a prominent example of a bottom-up, concurrent multiscale method aiming at a seamless link of atomic with continuum length scales. This aim is achieved by three main building blocks (i) a coarse-graining of fully atomic resolution via finite element discretization in order to reduce the number of degrees of freedom. Fully atomic resolution is retained at hot spots of inelastic deformations like at crack tips, at defect cores or alike, whereas a finite element coarse-graining is applied in regions of purely elastic deformation. (ii) An approximation of the energy/forces in coarse-grained regions via numerical quadrature which avoids the explicit computation of the site energy of each and every atom. (iii) Adaptivity, i.e. spatially adaptive resolution, is necessary to provide full atomic resolutions in regions of evolving or moving inelastic deformations like in crack propagation or microstructural evolution.
In [Eidel & Stukowski 2009] we develop a novel QC approach aiming at a truly seamless transition from the atomic to the continuum description of crystalline solids at zero temperature. It heavily draws on the framework proposed by Knap and Ortiz (2001). Opposed to Knap and Ortiz, the energy instead of forces is subject to a cluster based sampling scheme with adaptive resolution. We show that only the present ansatz endows the QC theory with a variational structure. The fully nonlocal methodology is assessed in nanoindentation into an fcc single crystal. Compared to the fully atomistic counterpart of lattice statics, the coarse-grained atomistic description with adaptive resolution achieves good agreement with respect to the force-displacement curve, the load-level and locus of dislocation nucleation and the dislocation microstructure for a small fraction of the computational costs. The figure shows the dislocation microstructure below the surface of an fcc aluminum single crystal which is subject to ball indentation at the nanoscale.
More recent research has been concerned with free surface relaxations of nano-structures in collaboration with N.V. Prajapati (RUB). Ongoing research activities are focused on modeling extensions of the QC but also with the development of novel numerical features for the method.
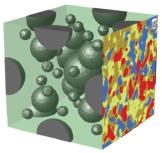
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project SCHR 570/12-1 Two-scale homogenization of magneto-electric composites
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, M.-A. Keip, M. Labusch
- Abstract:
Magneto-electric functional materials are of high technical relevance for the advancement and development of new functional devices in medical engineering and information technology. However, these materials become only technologically relevant when the desired coupling between magnetic and electric properties is present in a technically reasonable temperature range. Since this is not the fact for naturally occurring materials, the design of synthetic composite materials is of high scientific importance.
Within the scope of this project magneto-electric composites, consisting of a piezoelectric matrix with magnetic inclusions are modeled and analyzed micromechanically and characterized macroscopically. In order to do so, a fully magneto-electro-mechanically coupled, thermodynamically consistent model is developed for each individual phase on the microscale. Using computational homogenization the (effective) macroscopic response is determined, from which the desired magneto-electric coefficients can be computed.
This project is part of the DFG research group FOR 1509 "Ferroische Funktionsmaterialien - Mehrskalige Modellierung und experimentelle Charakterisierung" (project P1: "Design and analysis of functional composite materials with strain-induced magneto-electric coupling")

European Union Marie Curie Initial Training Network "NANOMOTION" FE simulation of piezoresponse force microscopy
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, M.-A. Keip, H. Thai
- Abstract:
Piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) is a type of the scanning-probe microscopy techniques which can be used to characterize the microstructure of ferroelectric materials. It can be applied for instance to study domain structures and the structure of domain walls. The working principle of the PFM technology is based on the measurement of the local piezoelectric deformation of a probe caused by an electric loading that is applied by a tip of a scanning force microscope.
The project investigates PFM by means of numerical simulation based on the phase-field method. The phase-field model is implemented into a finite element environment in order to study the domain evolution in ferroelectrics under applied electric tip loading. The results of the numerical model will be compared to measurements which are elaborated at the Institute for Materials Science of Professor Doru C. Lupascu.
This project is part of the European Union Marie Curie Initial Training Network (ITN) "Nanoelectromechanical motion in functional materials (NANOMOTION)" (project 1D: "Finite-element modelling of electromechanically coupled materials")
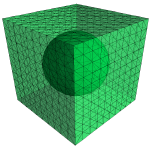
Computational homogenization of electro-mechanically coupled solids
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, M.-A. Keip
- Abstract:
Electro-mechanically coupled solids as piezo- and ferroelectric ceramics are in general polycrystalline materials and possess a heterogeneous micro- and mesostructure. Therefore, the overall macroscopic behavior of a bulk ferroelectric is influenced by the physical and geometrical constitution of the underlying micro- and mesostructure. A bulk macroscopic ferroelectric is generally composed of grains (polycrystalline ferroelectrics) or artificially constructed mesostructures that are composed of at least one piezoelectric phase (piezocomposites). In each case, the overall macroscopic behavior as well as the individual fields on the lower scales are of special interest, since both are important for the functionality of the piezoactive ceramic.
The project deals with the two-scale simulation of electro-mechanically coupled materials by means of the FE^2-method. In this connection, the focus is on the computation of effective material parameters and the analysis of mesoscopic electro-mechanical fields.
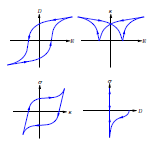
Modeling of nonlinear phenomena in ferroelectric solids
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, M.-A. Keip
- Abstract:
When applied to high electrical and/or mechanical fields, the constitutive response of ferroelectric materials becomes highly nonlinear and expresses itself in terms of e.g. dielectric-, butterfly-, and ferroelastic-type hysteresis. This is due to the fact that high electro-mechanical fields induce internal switching of the existing spontaneous polarization within the material. Such switching is utilized during the plarization process of a polycrystalline ferroelectric in order to produce a macroscopically coupled functional electroceramic. On the other hand, during the operation of a poled piezoelectric device, high internal fields can arise and lead to electrically and mechanically induced switching. These fields influence the functionality of the ceramic in such a way that they can lead to a partial or complete depolarization of the material.
The research project deals with the continuum mechanical modeling of electrically and mechanically induced switching from a microscopic view point. The modeling is based on a fully tetragonal representation of the material including an energy-based concept for the incorporation of ferroelectric and ferroelastic switching.

DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) SPP 1568 A model for self-healing anisotropic composites
- Associated people:
J. Bluhm, J. Schröder, S. Specht
- Abstract:
Self-healing materials belong to the class of smart materials. These materials can change their properties due to external influences. Inspired by biological systems, the development and manufacture of self-healing materials in view of new applications in engineering, material science and medicine is a subject of international research.
The aim of the research project is to develop a continuum-based micromechanical model and algorithms for the description of self-healing anisotropic composites. The fiber reinforced composites consist of a weak solid matrix and different fiber families, the healing process is based on the existence of healing agents embedded in the solid matrix. For the macroscopic description of these materials, an FE-discretization of the microstructure is used to fit the microscopic behavior to the homogenized macrostructure. The healing process of the matrix is modeled within the framework of the Theory of Porous Media (TPM), where criteria for the onset and progression of healing are formulated following experimental observations. The places of damage (cracks), the amount of healing agents as well the basic and the self-healed material can be identified by the corresponding volume fractions of a Representative Volume Element (RVE) in a finite element simulation.
- References:
J. Bluhm, S. Specht, and J. Schröder [2014], "Modeling of self-healing effects in polymer composites", Archive of Applied Mechanics
S. Specht, J. Bluhm, and J. Schröder [2014],"Modeling of self-healing phenomena in a polymer matrix based on a microcapsule system", WCCM
S. Specht, J. Bluhm, and J. Schröder [2014], " Modeling of self-healing phenomena in a polymer matrix within the framework of the theory of porous media", Proceedings in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,submitted
S. Specht, J. Bluhm, and J. Schröder [2013], "Fe-analysis of concentration dependent healing processes in a polymer matrix", Proceedings in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (Pages 219-220)
S. Specht, J. Bluhm, and J. Schröder [2013], "Self-healing phenomena in polymers based on the Theory of Porous Media", ICSHM 2013
S. Specht, J. Bluhm, and J. Schröder [2012], "Modeling of healing processes in a polymer matrix", Proceedings in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (Pages 357-358)
Specht S., Bluhm J. & Schröder J. [2012], "Modeling of Healing Processes in a Polymer Matrix", PAMM, accepted for publication

DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project BL 417/6-1,2 Ice Formation and Capillary Effects in Saturated Porous Media
- Associated people:
J. Bluhm, T. Ricken (TU Dortmund), W.M. Bloßfeld
- Abstract:
In civil engineering, the processes of freezing and thawing of fluid and gas saturated porous media is a point of great discussion. In addition they are strongly influenced by the fluid-ice phase transition. Ice formation in porous media results from coupled heat and mass transport and is accompanied by ice expansion. In a multiphase approach, a macroscopic quadruple model consisting of the constituents solid (cement stone), liquid (freezable water), ice and gas is developed within the framework of the Theory of Porous Media (TPM). The usefulness of the model for saturated porous solids under cycling thermal loading is demonstrated by a comparison of computationally and experimentally gained data of the CIF-Test (Capillary suction, Internal damage and Freeze-Thaw Test). Beside the influence of the heat of fusion, especially, the capillary suction as well as frost suction in gas and liquid filled porous media will be studied.
- References:
Ricken, T & Bluhm, J. [2010], "Modeling fluid saturated porous media under frost attack", GAMM-Mitt., Vol. 33 (1), pp. 40-56.Bluhm, J., Ricken, T., & Blossfeld, M. [2009], "Dynamic Phase Transition Border under Freezing-Thawing Load in Porous Media -- A Multiphase Description", Schroeder, J. (ed.): Report 47, Institute of Mechanics, University Duisburg-Essen, Germany.
Bluhm, J. and Ricken, T. & Blossfeld, M. [2009], "Freezing and thawing load in porous media - Experiment and Simulation", PAMM, Vol. 9, pp. 387 -388.
Bluhm, J. & Ricken, T. & Blossfeld, M. [2008], "Energetische Aspekte zum Gefrierverhalten von Wasser in porösen Strukturen", PAMM, Vol. 8, pp. 10483 - 10484.
Modeling_of_ionic_electroactive_polymers_-_consistent_formulation_of_the_thermoelectro-chemo-mechanical_coupling_effects_and_finite-element_discretization
- Associated people:
J. Bluhm, J. Schröder and S. Serdas
- Abstract
Multifunctional materials like Electroactive Polymers (EAPs) belong to the class of smart materials. These materials can change their properties due to external influences and/or active energy supply. Inspired by the behavior of biological systems, the development and manufacture of EAPs in view of new applications in engineering, material science and medicine is a subject of international research. The aim of the research project is the development of a continuum-based model and its algorithmic implementation for the description of the behavior of ionic (wet) EAPs. These materials consist of a network of polymer fibers, the pore space is filled with liquid and gas. The deformation of ionic EAPs is driven by the motion of anions and cations (diffusion) triggered by an electric field. An advantage of ionic EAPs is that only a few volts are needed for the actuation, the disadvantage is that they must be kept moist. For the continuum mechanical based description of the behavior of these multiphase materials, consisting of the phases solid (polymer matrix), liquid, gas (vapor) and ions, the Theory of Porous Media will be used. In view of the electro and thermo-chemomechanical coupling effects in ionic EAPs, the balance equations of electrodynamics will be considered. Predictions concerning an efficient mode of avtion of the ionic EAPs depending on the humidity of the polymer matrix shall be enabled.
- Further information
http://chemomechanics.de/projects/
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project SCHR570/14-1 Least-squares mixed finite element formulations for solid mechanics
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, A. Schwarz, K.Steeger, in cooperation with G. Starke (Leibniz University Hannover)
- Abstract:
For the solution of partial differential equations describing physical problems in the framework of solid mechanics, we develop in this project least-squares mixed finite element formulations and examine their performance. Starting from the balance of momentum, we obtain div-grad first-order systems with e.g. stresses and displacements as unknowns and by means of quadratic L2-norms a least-squares functional can be constructed. This functional is the basis for the associated minimization problem, which is not restricted to the LBB-condition. Moreover, due to some additional advantages, as e.g. a smooth stress approximation even for quasi-incompressible materials and an a posteriori error estimator without additional costs, least-squares variational principles have increasingly gained attention.
- References
Schwarz, A., Schröder, J. & Starke, G. [2010], “A modified Least-Squares Mixed Finite Element with improved Momentum Balance”, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 81, p. 286-306.Schwarz, A. [2009], “Least-Squares Mixed Finite Elements for Solid Mechanics”, Dissertation, Institut für Mechanik, Bericht 7, Universität Duisburg-Essen.
Schwarz, A., Schröder, J. & Starke, G. [2009], “Least-Squares Mixed Finite Elements for Small Strain Elasto-Viscoplasticity”, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 77, p. 1351-1370.
Mercator Research Center Ruhr, project PR-2011-0017 Computational Fluid Dynamics
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, A. Schwarz, S. Serdas, in cooperation with S. Turek (TU Dortmund)
- Abstract:
The main focus of this project is to examine least-squares mixed finite elements for the solution of steady and unsteady Newtonian fluid flow, which is described by the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations.
Least-squares variational principles have increasingly gained attention, which is due to some theoretical and computational advantages compared to the Galerkin method.
- The method provides for instance an a posteriori error estimator without additional costs, which can be used for the development of adaptive mesh refinement algorithms.
- The resulting symmetric positive definite system matrices can be solved by using robust and fast iterative methods even for problems with governing nonselfadjoint operators such as fluid dynamics and transport problems.
- The inf-sup condition does not hold, so there are no restrictions for the choice of the polynomial degree of the finite element spaces.
The development and improvement of mixed least-squares finite element formulations by means of these topics are the main incentive of our research.
In general, we consider div-grad first-order systems resulting in approaches with e.g. stresses, velocities, and/or pressure as unknowns. The L2-norms of the residuals of the derived equations yield then the least-squares functional, which is the basis for the associated minimization problem.
- References
Cai, Z. and Lee, B. and Wang, P.[2004], “Least-squares methods for incompressible Newtonian fluid flow: linear stationary problems”, SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 42, p. 843-859.Schwarz, A. and Schröder, J. [submitted], “A mixed least-squares formulation of the Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible Newtonian fluid flow”, PAMM Proceedings in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics.
Münzenmaier, S. and Starke,G. [2011], “First-order system least squares for coupled Stokes-Darcy flow”, SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 49, p. 387--404.

Mixed Finite Element Formulation based on Different Approximations of the Minors of Deformation Tensors
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, D. Balzani (TU Dresden), in cooperation with P. Wriggers (Leibniz University Hannover)
- Abstract:
Finite element formulations for arbitrary hyperelastic strain energy functions that are characterized by a locking-free behavior for incompressible materials, a good bending performance and accurate solutions for coarse meshes need still attention. Therefore, the main goal in this project is to provide an improved mixed finite element for quasi-incompressible finite elasticity. Based on the knowledge that the minors of the deformation gradient play a major role for the transformation of infinitesimal line-, area- and volume elements, as well as in the formulation of polyconvex strain energy functions a "double mixed" finite element with different interpolation orders of the terms related to the minors is developed. Due to the formulation it is possible to condensate the mixed element formulation at element level to a pure displacement form.

DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) SPP (German Priority Program) 1748 Novel finite elements for anisotropic media
- Associated people
J. Schröder and N. Viebahn in cooperation with P. Wriggers (Leibniz University Hannover) and D. Balzani (TU Dresden)
- Abstract
Considering solid mechanics, a majority of the problems can be solved using the standard Galerkin method. Although this method is used as a standard tool for predicting the behavior of a variety of engineering structures, certain problems limit the applicability. In general, incompressible and/or anisotropic materials could lead to not well-posed formulations.
Finite-element formulations, which are available today using a purely volumetric-isochoric split, are not sufficient for anisotropic materials. Therefore, in this research project, the primary goal is to develop new finite-element formulations as a suitable basis for the stable calculation of complex materials in nonlinear applications. In order to achieve this goal new ideas have to be pursued since there is no obvious approach available at the moment to overcome these difficulties. Therefore, we follow three main strategies:
- Different approximations of the kinematic quantities entering the isotropic and anisotropic parts of the free energy function provide the possibility to relax the constraints arising from anisotropy. In this approach the structure of the polyconvex energy function is preserved.
- Special approximations of the minors of the deformation gradient lead to mixed formulations suitable for more general polyconvex strain energy functions. Thereby the ansatz spaces for the mixed variables approximating the minors are balanced.
- The VFEM, which was formulated so far only for small strain problems, is extended to large strains based on isotropic/anisotropic polyconvex strain energy functions. Thereby, the advantage to discretize non-convex regions using VFEM is exploited for the application to highly distorted deformed meshes.
As a common software development platform both workgroups, Essen and Hannover, will apply the AceGen environment which provides a flexible tool for the generation of efficient finite element code. This is in particular important because of the high complexity of the mixed forms and the large number of different variants to be considered.
- Mechanical-, civil- and aerospace engineering: Robust finite-element technologies will make highly predictible simulations available to various engineering applications and reduce development times and costs.
- Software industry: More reliable finite elements will help to build simulation environments that predict more realistically the behavior of various physical problems.
- Clinical medicine: The reliable prediction of the behavior of soft biological tissues will provide decision support for clinical doctors, e.g. for cardiovascular treatments.
- Biomedical engineering: The development of artificial implants, as e.g. stents, will be performed more efficiently based on stable numerical simulations, and the number of animal tests will be dramatically reduced.

DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project 1748 ("Reliable simulation techniques in solid mechanics First-order system least squares finite elements for finite elasto-plasticity
- Associted people
G. Starke, A Schwarz, J. Schröder and Maximilian Igelbüscher
- Abstract
The goal of this project is to reveal the potential of mixed finite element approaches based on first-order system least squares formulations for finite elasto-plastic deformations in nonlinear solid mechanics. This rests upon recent and ongoing work of the participating investigators studying stress-displacement first-order system approaches for small-strain elasto-plasticity and finite (hyper-)elasticity. The interest in this class of methods is driven by the need of accurate stress approximations with good momentum balance properties observed in various high-tech applications, as for instance from the automobile or aircraft industry (e.g. light-weight constructions) or from biomedical research (e.g. arterial wall/stent simulations). To the best knowledge of the authors there are no reliable and verified approaches for finite elasto-plasticity computations available at the moment and the main incentive of this project is to contribute in closing this gap.
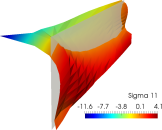
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project SCHR 570/16-1 Simulation of residual stresses in arterial walls
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, S. Brinkhues, M. von Hoegen
- Abstract:
In a variety of investigations of the mechanical behavior of arteries it is assumed, that an unloaded artery exhibits an internal zero-stress state. This assumption does not reflect the real behavior, which can be observed in experiments: when an axial section is cutted in longitudinal direction, the artery springs open. This ``cutted'' configuration is often assumed to be stress-free. In various works dealing with the numerical simulation of arterial walls, it is accounted for residual stresses by closing an opened, unstressed artery by an initial bending to form a load-free, but internally stressed configuration. However, such configuration is not available for real purposes. In this research project we propose a novel approach for the incorporation of residual stresses in human arteries. In contrast to the approach described above, we focus directly on the gradients of appropriate stresses in radial direction. Motivated by the arrangement of the embedded fibers, the gradients of the fiber stresses in radial direction are considered and smoothed by dint of residual stresses. This approach is applicable for arbitrary two- or three-dimensional arterial geometries and thus an appropriate solution for such complex physiological problems.

DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project SCHR 570/15-1 and 570/15-2, in cooperation with SNF (Swiss National Science Foundation) under the D-A-CH agreement Domain-Decomposition-Based Fluid Structure Interaction Algorithms for Highly Nonlinear and Anisotropic Elastic Arterial Wall Models in 3D
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, D. Balzani (TU Dresden), S. Fausten, in cooperation with A. Klawonn (Universität zu Köln), O. Rheinbach(TU Freiberg), A. Quarteroni, S. Deparis (EPF Lausanne)
- Abstract:
Transmural stress distributions of in vivo arteries are a major factor driving, e.g., the processes of arteriosclerosis and arteriogenesis. Realistic predictions for transmural stress distributions require a dynamic simulation considering the interaction of the blood flow with the vessel wall. One cannot expect to obtain precise predictions for vessel wall stresses using solid models that do not reflect the global layer structure and the anisotropic fibrous microstructure of the vessel wall. Furthermore, eigenstress distributions in the vessel wall must be taken into account for the analysis of more realistic stress regimes and can be observed to have significant influence on simulations. The fluid-structure-interaction (FSI) problem is known to be a nontrivial problem especially when nonlinear models are used for the structural part describing the deformation of the arterial wall. In this project, algorithms for the fluid-structure interaction are developed based on domain decomposition methods and applied to the computation of realistic transmural stresses in physiological models of arterial walls. The associated systems of coupled nonlinear partial differential equations are to be solved in 3D and on different parallel machines. Moreover, a biologically motivated model for the incorporation of residual stresses is constructed based on nonlocal stress measures.
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project SCHR 570/6-2, KL 2094/1-2 Large scale simulation of arterial walls using FETI-DP
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, D. Brands, S. Brinkhues, D. Balzani (TU Dresden), in cooperation with A. Klawonn (Universität zu Köln), O. Rheinbach(TU Freiberg), R. Erbel (Westdeutsches Herzzentrum Essen)
- Abstract:
In order to improve the blood flow in artherosclerotic arteries an extension of the lumen is essential. An often used method of treatment is the balloon-angioplasty, whose success requires the knowledge of the mechanics of arterial walls. Thus the numerical simulation provides a method to analyse the deformation behavior of the arterial wall and its constituents under the loading by a ballon-angioplasty. The necessary 3D-discretizations by finite elements results in large systems of equations, therefore, a parallel algorithm using FETI-DP is applied to solve the equilibrium problem.
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project BA 2823/5-1, in cooperation with FWF (Austrian Science Fund) under the D-A-CH agreement Biomechanics of Arterial Walls under Supraphysiological Loading Conditions
- Associated people:
D. Balzani (TU Dresden), T. Schmidt, in cooperation with G. A. Holzapfel (TU Graz)
- Abstract:
This research project deals with the analysis and the modeling of traumatic degenerations of overstretched arterial walls that occur in therapeutical interventions. The data base for the qualitative and quantitative description of arterial tissues is obtained from biaxial extension tests performed on the tissue components of individual arterial layers loaded far beyond the physiological domain. Such tests enable the analysis of the macroscopic mechanical response of the tissues. In addition, structural analysis techniques such as Fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy are used to study damage on the smaller length scale. The macroscopic response of the fiber-reinforced tissues is described by a formulation based on micro-mechanical models characterizing the individual tissue components. These models take into account alterations of stochastic distributions of fiber properties as a consequence of the tissue overstretch. In order to obtain a quantitative prediction of the material response the model parameters are adjusted to the performed experiments based on least-square minimization. Finally, we validate the models by comparing finite element calculations with experiments performed on whole arterial wall segments.
- References:
Balzani, D., Brinkhues, S. & Holzapfel, G. (2012), "Constitutive Framework for the Modeling of Damage in Collagenous Soft Tissues with Application to Arterial Walls", Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. Vol. 213--216, pp. 139-151.
Balzani, D., Neff, P., Schröder, J. & Holzapfel, G. (2006), "A Polyconvex Framework for Soft Biological Tissues. Adjustment to Experimental Data", International Journal of Solids and Structures. Vol. 43(20), pp. 6052-6070.
DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) project NE 902/2-2, SCHR 570/6-2 Construction of Anisotropic Polyconvex Energies on the Basis of Anisotropic Metrics
- Associated people:
J. Schröder, P. Neff, V. Ebbing
- Abstract:
In order to guarantee the existence of minimizers of the underlying potential in finite elasticity, a suitable concept is the polyconvexity condition of the energy function in the sense of Ball 1977. Until recently, the construction of polyconvex energy functions for the description of anisotropic material behavior was a question yet to be answered. The first transversely isotropic and orthotropic polyconvex energy functions were presented by Schröder and Neff in the years 2001, 2003. In the present work a method for the construction of polyconvex, coordinate-invariant energy functions for the description of all existing anisotropic hyperelastic materials is proposed. The key idea is the introduction of so-called crystallographically motivated structural tensors. The applicability of this method is shown within several numerical examples.
DFG_Deutsche_Forschungsgemeinschaft_research_fellowship_project_BA_2823_6-1 Relaxed Incremental Variational Formulation for Damage at Large Strains with Application to Fiber-Reinforced Materials and Materials with Truss-like Microstructures
- Associated people:
D. Balzani (TU Dresden), in cooperation with M. Ortiz (CALTECH Pasadena)
- Abstract:
In this project incremental variational formulations for damage at finite strains are developed. The classical continuum damage mechanics serves as a basis where a stress-softening term depending on a scalar-valued damage function is prepended an effective hyperelastic strain energy function, which describes the virtually undamaged material. Since loss of convexity is obtained at some critical deformations a relaxed incremental stress potential is constructed which convexifies the original non-convex problem. The resulting model can be interpreted as the homogenization of a micro-heterogeneous material bifurcated into a strongly and weakly damaged phase at the microscale. A one-dimensional relaxed formulation is derived and based thereon, models for fiber-reinforced materials are constructed. Moreover, these models are used for the computational homogenization of materials with truss-like microstructures as e.g. cellular materials.
>>Top>#oben

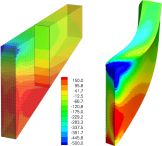
Indentation in Crystal Plasticity - Finite Element Simulation and Comparison with Experiments
- Associated people:
B. Eidel, J. Schröder - Abstract:
Pyramidal microindentation into the (001) surface of an fcc single crystal has shown indent shapes which strongly depend on the azimuthal orientation of the pyramid, see the left column of the adjacent figure. This observation is experimentally elucidated by means of high resolution electron back-scatter diffraction (EBSD) technique along with digital image processing creating a digital surface model. The main findings are that pile-up formation is invariantly maximum in <110> directions (4 hillocks emerge) thus being independent of the azimuthal orientation of the pyramid. For different orientations of the indenter the material pile-up is locally accommodated to the indenter faces leading to a convex, a concave or a mixed curved contact rim at the faces of the indenter. The right column in the figure shows, that crystal plasticity finite element simulations are in good agreement with the observed surface deformation pattern. The influence of stress concentration onto the anisotropic pile-up is negligible. This is corroborated on the relative invariance of pile-up for different indenter orientations (an anisotropy in loading). The driving mechanism behind the observed phenomena is plastic glide in (111) <110> slip systems.
- References

Development of High-order time-integration Methods for Inelastic Constitutive Laws
- Associated people:
B. Eidel, C. Kuhn (LTM, Uni Kaiserslautern), J. Schröder - Abstract:
Time integration is the numerical kernel of inelastic finite element calculations, which largely determines their accuracy and efficiency. If higher order Runge–Kutta (RK) methods, p>2, are used for integration in a standard manner, they do not achieve full convergence order but fall back to second-order convergence. This deficiency called order reduction is a longstanding problem in computational inelasticity. We analyze it for viscoelasticity, where the evolution equations follow ordinary differential equations (ODE). We focus on RK methods of third order. We prove that the reason for order reduction is the (standard) linear interpolation of strain to construct data at the RK-stages within the considered time interval. We prove that quadratic interpolation of strain based on t_(n), t_(n+1) and, additionally, t_(n-1) data implies consistency order three for total strain, viscoelastic strain and stress. Simulations applying the novel interpolation technique are in perfect agreement with the theoretical predictions. The present methodology is advantageous, since it preserves the common, staggered structure of finite element codes for inelastic stress calculation. Furthermore, it is easy to implement, the overhead of additional history data is small and the computation time to obtain a defined accuracy is considerably reduced compared with backward Euler.
Ongoing research work has been focused on the more delicate problem of order reduction in elasto-plasticity. This broad class of inelastic continuum constitutive laws is usually described by ordinary differential equations for the evolution of plastic flow, which is subject to the yield condition as an algebraic constraint, thus forming altogether a set of differential algebraic equations (DAE).
- References


