GRK 2762 - Research Projects

Project T 1Biomarkers of pneumonitis and lung fibrosis upon thoracic RT/RCTx with or without concomitant anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy
Principal Investigators
Prof. Dr. med. Nika Guberina
Department of Radiotherapy
University Hospital Essen
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Verena Jendrossek
Institute of Cell Biology (Tumor Research)
University Hospital Essen
Participating Senior Scientist
Dr. Florian Wirsdörfer
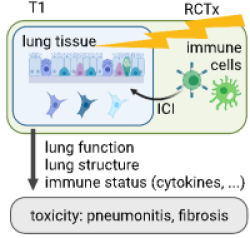
Summary
PhD Project
Immune-related adverse effects (irAE) are dose limiting for radiotherapy (RT) ± immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Currently, diagnosis is made by exclusion based on clinical assessment, pulmonary function tests, and radiological findings, but predisposing factors and biomarkers are less defined. This project aims to examine the complex mechanism of action of ICI therapy combined with RT and/or chemotherapy with regard to immune-related lung tissue reactions and pulmonary radiotoxicity in patients and in a co-clinical murine model. We speculate that cytokine levels in serum and bronchioalveolar lavage, as well as the myeloid and lymphocytic landscape, may help to distinguish different types of pneumonitis. We will record numerous baseline conditions and time resolved functional abnormalities in both, lymphoid and myeloid alveolar cell types, and investigate their role as potential risk drivers and contributors of therapy-induced lung disease. Patients with virus-related lung tissue damage will serve as controls. Overall goal is to identify predisposing risk and biomarker patterns for early detection of different types of irAE in the lung and thereby to improve multimodal treatment in NSCLC patients.
Clinician scientist project
The clinician scientist will differentiate various types of lung tissue reaction and injury of NSCLC patients undergoing neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy without or with ICI-therapy in the randomized investigator-initiated trial ESPADURVA at UK Essen (PIs, W. Eberhardt, M. Stuschke). All patients in whom a pneumonitis and fibrotic lung changes of different etiologies develop during the course of disease and treatment will undergo the following special diagnostic sequence: i) clinical examination; ii) functional lung tests; iii) blood serum tests; iv) radiological assessment. Bronchial brushes and washes and BAL, are performed, if clinically indicated. Infectious causes will be determined by sputum cultures and BALF (if clinically indicated). After exclusion of infectious causes (sputum cultures and BAL, if indicated) and tumor progression (computed-tomography (CT), [68Ga]FAPI- and [18F]FDG-positron emission tomo-graphy (PET)/CT), immune-related pneumonitis will be diagnosed by the presence of clinical symptoms and typical radiographic infiltrates on radiographs, CT and PET/CT. Radiological findings will be correlated with clinical and laboratory findings with respect to dose exposure of high, intermediate, and low-density areas in the lung in relation to pneumonitis or fibrosis development.
Selected Publications
Prof. Dr. Nika Guberina
Guberina N, Pöttgen C, Schuler M, Guberina M, Stamatis G, Plönes T, Krebs B, Metzenmacher M, Theegarten D, Gauler T, Jöckel KH, Darwiche K, Aigner C, Stuschke M, Eberhardt WE. Comparison of early tumour-associated versus late deaths in patients with central or >7 cm T4 N0/1 M0 non-small-cell lung-cancer undergoing trimodal treatment: Only few risks left to improve. Eur J Cancer. 2020 Oct;138:156-168. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.07.025.
Bos D, Zensen S, Opitz MK, Haubold J, Nassenstein K, Kinner S, Schweiger B, Forsting M, Wetter A, Guberina N. Diagnostic reference levels for chest computed tomography in children as a function of patient size. Pediatr Radiol. 2022 Apr 5. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05340-8.
Guberina M, Poettgen C, Metzenmacher M, Wiesweg M, Schuler M, Aigner C, Ploenes T, Umutlu L, Gauler T, Darwiche K, Stamatis G, Theegarten D, Hautzel H, Jentzen W, Guberina N, Herrmann K, Eberhardt WEE, Stuschke M. PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF POST-INDUCTION CHEMOTHERAPY VOLUMETRIC PET/CT PARAMETERS FOR STAGE IIIA/B NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER PATIENTS RECEIVING DEFINITIVE CHEMORADIOTHERAPY. J Nucl Med. 2021 May 20;62(12):1684–91. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.260646.
Guberina M, Darwiche K, Hautzel H, Ploenes T, Pöttgen C, Guberina N, Herrmann K, Umutlu L, Wetter A, Theegarten D, Aigner C, Eberhardt WEE, Schuler M, Karpf-Wissel R, Stuschke M. Impact of EBUS-TBNA in addition to [18F]FDG-PET/CT imaging on target volume definition for radiochemotherapy in stage III NSCLC. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Aug;48(9):2894-2903. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05204-7.
Guberina N, Hetkamp P, Ruebben H, Fendler W, Grueneisen J, Suntharalingam S, Kirchner J, Puellen L, Harke N, Radtke JP, Umutlu L, Hadaschik BA, Herrmann K, Forsting M, Wetter A. Whole-Body Integrated [68Ga]PSMA-11-PET/MR Imaging in Patients with Recurrent Prostate Cancer: Comparison with Whole-Body PET/CT as the Standard of Reference. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Jun;22(3):788-796. doi: 10.1007/s11307-
Prof. Dr. Verena Jendrossek
Heinzelmann F, Jendrossek V, Lauber K, Nowak K, Eldh T, Boras R, Handrick R, Henkel M, Martin C, Uhlig S, Köhler D, Eltzschig HK, Wehrmann M, Budach W, Belka C. Irradiation induced pneumonitis is mediated by the CD95/CD95-ligand system. J Nat Canc Inst. 2006; 98. 1248-1251. DOI: 10.1093/JNCI/DJJ335
Wiesemann A, Ketteler J, Slama A, Wirsdorfer F, Hager T, Rock K, Engel DR, Fischer JW, Aigner C, Jendrossek V, Klein D. Inhibition of Radiation-Induced Ccl2 Signaling Protects Lungs from Vascular Dysfunction and Endothelial Cell Loss. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019;30(2):213-231. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7458
de Leve S, Wirsdorfer F, Cappuccini F, Schutze A, Meyer AV, Rock K, Thompson LF, Fischer JW, Stuschke M, Jendrossek V. Loss of CD73 prevents accumulation of alternatively activated macrophages and the formation of prefibrotic macrophage clusters in irradiated lungs. FASEB J. 2017;31(7):2869-2880. DOI: 10.1096/fj.201601228R
Westendorf AM, Skibbe K, Adamczyk A, Buer J, Geffers R, Hansen W, Pastille E, Jendrossek V. Hypoxia Enhances Immunosuppression by Inhibiting CD4+ Effector T Cell Function and Promoting Treg Activity. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1271-1284. DOI: 10.1159/000464429
Wirsdorfer F, de Leve S, Cappuccini F, Eldh T, Meyer AV, Gau E, Thompson LF, Chen NY, Karmouty-Quintana H, Fischer U, Kasper M, Klein D, Ritchey JW, Blackburn MR, Westendorf AM, Stuschke M, Jendrossek V. Extracellular Adenosine Production by ecto-5'-Nucleotidase (CD73) Enhances Radiation-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Cancer Res. 2016;76(10):3045-3056. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2310

